ABOUT GGL 4C's
The cut of a diamond means its size and shape.Out of the Diamond 4 C’s,this feature of cut is mostly
pretended by man however the rest three are founded by mother nature. Generally, we see that
people make a confusion between the cut and the shape of a diamond. The diamonds can be cut
into different shapes that vary as per the original format of an uncut diamond, which is known as
rough.
 A well-cut diamond can reproduce the light much better than any other diamond. A diamond’s
demonstration of fire and brightness is controlled by its capacity to reflect the light. Usually, diamonds
are cut with distinct flat surfaces or 58 facets.These facets are based on a mathematical formula and
they are positioned at accurate angles those are associated with each other.The association is being
planned to make the most of the light that replicates through the diamond making it look more
beautiful.
A well-cut diamond can reproduce the light much better than any other diamond. A diamond’s
demonstration of fire and brightness is controlled by its capacity to reflect the light. Usually, diamonds
are cut with distinct flat surfaces or 58 facets.These facets are based on a mathematical formula and
they are positioned at accurate angles those are associated with each other.The association is being
planned to make the most of the light that replicates through the diamond making it look more
beautiful.
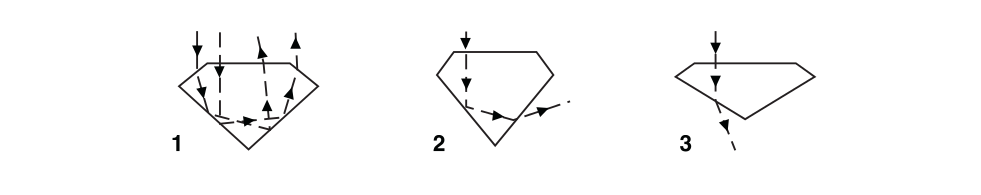
- Well Cut- When a diamond gets cut in the right magnitudes, the light reprocess in all the facets
and then gets distributed via the upper side of the stone. The well cut standards are divided into
three sub categories, namely, ideal, Excellent, and Very Good.
- Ideal- This range is too firm and it proves to be the best blend of fire and brilliance. Technically speaking, this is the head of all the ranges.
- Excellent- This range is a beautiful range and it is a bit flexible in respect to the proportion and percentages. This range is considered to be perfect.
- Very good- This range is well-adjusted between clear-cut proportions and price deliberations.Many people consider this range as the best because of price and beauty.
- Deep cut- when a diamond is cut very deeply, some light goes out from the opposite side of the pavilion.
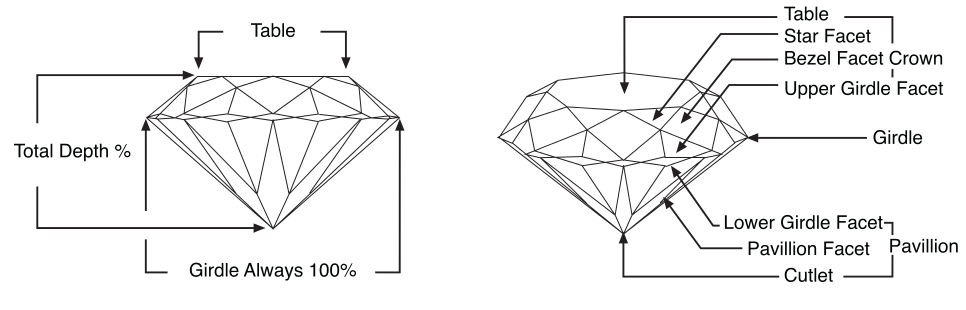
- Shallow Cut-When you find that a diamond’s cut is very shallow, light goes out via the pavilion before the process of reflection. Tauheed Manufacturing Jewellery The measurement of the cut or the proportions of a diamond are practiced in terms of percentage compared to the diameter of its girdle.Each diamond has a girdle diameter which is always supposed to be 100%.
How to recognize whether the diamond is well cut? A well cut diamond always looks beautiful and brilliant too. A well cut diamond can be found out easily. You can prefer a specific set of proportion or you may also pick up something else. There are three sub- categories by the Diamonds.com along with the proportions of well cut diamond so that you can select the best diamond for yourselves. Experts have established the categories on the grounds of long term research and the standard practices done by the experts and the laboratories. To understand the concept of the three sub categories, you can think them as rings in a bull's eye.The classification for the cut characterize a satisfactory range that belongs to that category. The range starts narrowing as you move forward to the Centre. The narrowest range belongs to the ideal, with best little large and very good at the largest. All the three categories come under the "well-cut" category. You may usually find that visual difference between two categories is so small that one can see them with naked eyes. Science has invented modern machinery to measure all the features of the diamond’s proportions. Precision will enable such strict diamonds to be demarcated. These guidelines will help you to choose a right cut and to know more about its scientific base.Under all the circumstances, you need to get a glittering and brilliant diamond.
The lowest score can be the average cut grade. With an intention to categorize all the diamonds on the grounds of overall cut grade, the lowest grade for an individual feature is always considered. The proportions vary from shape to shape. Many of the shapes of diamonds need their own guidelines to get maximum beauty.
Due to the mathematical differences essential in various shades, the guidelines of the depth are expressed to make best use of fire and brilliance. Though the numbers are dissimilar, motive remains the same.
Girdle The outer size of a diamond is known as Girdle. It usually has a frozen guise. There re many types of diamonds which are finished with complete polish or a faceted girdle.The value of the diamond has nothing to do with the features. The rating of girdle is done in terms of thickness. The size of the girdle is usually defined like Extremely Thin, Very Thin, Thin, Medium, Slightly Thick, Thick, Very Thick, or Extremely Thick. One can also describe the griddle in relation with these terms. While you purchase a diamond, you must pick one with a girdle that is not very thin or not very thick.
Cutlet The Bottom point of a diamond is known as cutlet. Most of the times, this point has a small facet. This is spoken f to in terms those are relevant with the presence of the facet or its size. The cutlet is normally graded as none or Pointed, Very Small, Small, Medium, Slightly Large, Large, Very Large, and Extremely Large. Smaller the better.
Polish This feature refers to the polishing or finishing of the facets or the flat surfaces. Generally diamonds are polished and ground and not fragmented till they become finished. The diamond cutter should very cautiously design each and every facet to make it glow and be perfect. The diamond polish is usually categorized as Poor, Fair, Good, Very Good, or Excellent. When you go to buy one, choose one that has polishing grades good or above.
Symmetry This feature is related to the alignment and standing of the facets, or flat surfaces.Each and every facet must be cautiously placed by the diamond cutter in the right proportion to others. The configuration of each facet should be high-pitched and precise.. The symmetry of a diamond is generally outlined as Poor, Fair, Good, Very Good, or Excellent. While you go to purchase diamonds, you should go for the one with a symmetry grade of Good or above.
Flourescence This aspect of the diamond is related to the capacity of a diamond to fluoresce in the presence of ultraviolet light. Many of the diamond will generate a different shining blue coloration when they are wide-open to UV light. Flourescence can be shown in different shades, however blue is most commonly found colour in diamonds. The fluorescence of a diamond is characterized by its strength may be none, Faint, Medium, Strong, or Very Strong. Usually the fluorescence is not problematic except the intensity is Strong or Very Strong. If the colors are very high, Strong fluorescence is not recommended. However, if the colors are lower, Strong fluorescence is looked-for.

If the diamond is having no color, then that can be best diamond. Diamonds permits light to reflect and get divided in rainbow form. The technical grading does not get affected by the colour flash or the light dispersion. The colorless stone has the rating plunging through each letter of the alphabet to Z, labeling a diamond of light yellow, brown, or gray. The boy color may be a result of the presence of some elements like nitrogen. These types of elements are very small and they can be measured scientifically in parts per million (ppm).

The more intense the body color, the lower is the grade of colour. These gradation is very minute an can be one in the laboratory only. It is always advisable to make the comparison of diamonds with the help of the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) or the American Gem Society (AGS) or that you can get the appropriate color grading. As far as the direct comparison of color of diamond is concerned, most of the people cannot find out the difference .You can take a diamond of grade k or above.

Fancy Colour People get very surprised after they come to know that diamonds also are made as a result of some accidents in shades of amber, green, pink or blue. These rare colours are known as fancies and they are estimated by a different set of color standards. These standards also consider many factors like hue and saturation. These fancy diamonds are very costly due to the uniqueness.
More or less all diamonds have a very small natural birthmarks, which are named as inclusions. Expert sees the diamonds under 10 power magnification in order to conclude it’s clarity. Besides to internal inclusions, the surface irregularities are known as blemishes. The two classes of inclusions and blemishes construct the clarity. Leser the blemishes, unique and more valuable the diamonds. Most of the inclusions cannot be seen by the naked eyes and they need magnification to be superficial.A clarity rating that is done in a laboratory epitomizes the point where inclusions are not actually visible to the normal naked eyes. Unlike the traditional belief, good clarity does not always represent the beauty. If the inclusions cannot be seen by the naked eyes, a good quality cannot actually enhance the view of a diamond, but it makes an impact on the uniqeness and the price. A good quality is more looked for and worth , however you should know that you have made the right choice. We recommend a clarity of SI2 or above.
The grading of the clarity is done by using accurate and a difficult method of finding out size, visibility and location. The right hand side diagrams present top view of the round diamond. The inclusions those are indicated in red colour are a rough sample for grading of clarity.You need to keep in mind that the inclusions described in red cannot be seen by an average naked eye unless they are having I1-I3 clarities.
| Flawless These do not represent any blemishes or inclusions of any types under 10x magnification when it is checked by a professional. |  |
| Internally lawless This does not have any inclusions when tested by a professional with 10x magnification, but it will contain some small blemishes. |  |
| VERY, VERY SLIGHTLY INCLUDED This has small inclusions those cannot be found out even by an expert under under 10x magnification. |  |
| VERY SLIGHTLY INCLUDED This has small inclusions like feathers, crystals or clouds when tested under 10x magnification. |  |
| SLIGHTLY INCLUDED These have some inclusion like knots, cavities or feathers. These can be viewed by an expert grader under 10x magnification. | 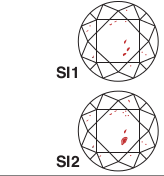 |
| INCLUDED Contains inclusions, probably big feathers or large crystals thos can be seen under 10x magnification and that make a difference to the transparency and brilliance. | 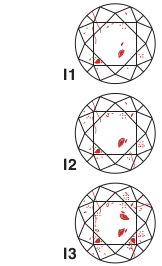 |
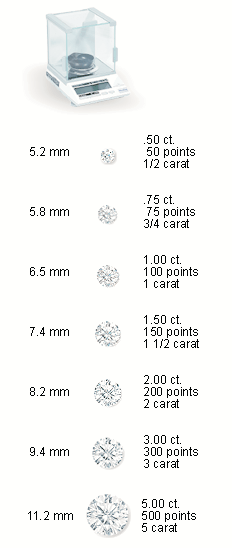
Generally carat weight is compared to the size. The bigger the diamond, the more is its weight. The weight of a diamond is calculated in carats. The word carat is invented from the carob tree or Ceratonia siliqua. The small seeds of the three are best known for their homogeneity and steady weight.In earlier times,diamonds and gemstones were calculated in contrast to these seeds, but later on the standards came into existence and one carat was agreed to be at 0.2 grams. One carat gets fractioned into 100 points. A diamond of which the weight is one quarter of a carat can also be referred as weighing 25 points or 0.25 carats.Usually they do not make use of the points to describe the weights for one carat. For better understanding we hereby give some examples of several weights for round diamonds and their relative sizes and shapes. These may not be the correct size because of the monitor. The fairly accurate girdle diameter is expressed in millimeters. What difference the sizes make the rarity The size makes a great difference to the rarity. The rarity of 1.00 carat diamond is almost double of .50 carat.However, the 1.00 carat is technically very unique than the .50 carat. |
 |